The oldest mummies in the world may hail from southeastern Asia and date back 12,000 years
Advertisement
Read this article for free:
or
Already have an account? Log in here »
To continue reading, please subscribe:
Monthly Digital Subscription
$0 for the first 4 weeks*
- Enjoy unlimited reading on winnipegfreepress.com
- Read the E-Edition, our digital replica newspaper
- Access News Break, our award-winning app
- Play interactive puzzles
*No charge for 4 weeks then price increases to the regular rate of $19.00 plus GST every four weeks. Offer available to new and qualified returning subscribers only. Cancel any time.
Monthly Digital Subscription
$4.75/week*
- Enjoy unlimited reading on winnipegfreepress.com
- Read the E-Edition, our digital replica newspaper
- Access News Break, our award-winning app
- Play interactive puzzles
*Billed as $19 plus GST every four weeks. Cancel any time.
To continue reading, please subscribe:
Add Free Press access to your Brandon Sun subscription for only an additional
$1 for the first 4 weeks*
*Your next subscription payment will increase by $1.00 and you will be charged $16.99 plus GST for four weeks. After four weeks, your payment will increase to $23.99 plus GST every four weeks.
Read unlimited articles for free today:
or
Already have an account? Log in here »
NEW YORK (AP) — Scientists have discovered what’s thought to be the oldest known mummies in the world in southeastern Asia dating back up to 12,000 years.
Mummification prevents decay by preserving dead bodies. The process can happen naturally in places like the sands of Chile’s Atacama Desert or the bogs of Ireland where conditions can fend off decomposition. Humans across various cultures also mummified their ancestors through embalming to honor them or send their souls to the afterlife.
Egypt’s mummies may be the most well-known, but until now some of the oldest mummies were prepared by a fishing people called the Chinchorro about 7,000 years ago in what’s now Peru and Chile.
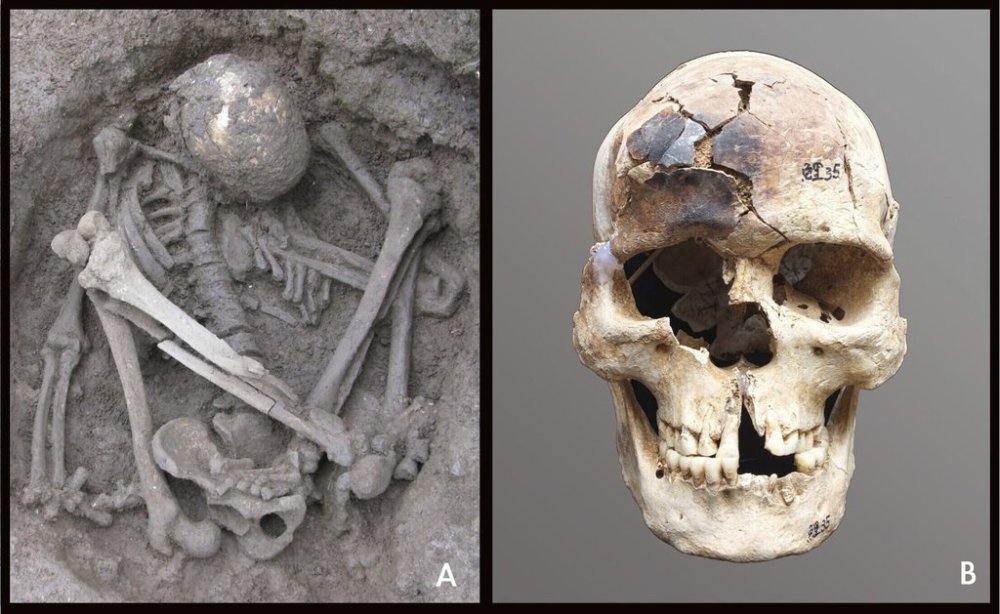
A new study published Monday in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences pushes that timeline back.
Researchers found human remains that were buried in crouched or squatted positions with some cuts and burn marks in various archaeological sites across China and Vietnam and to a lesser extent, from the Philippines, Laos, Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia.
Studying the bones further, scientists discovered the bodies were likely exposed to heat. That suggested the bodies had been smoke-dried over a fire and mummified by hunter-gatherer communities in the area.
The practice “allowed people to sustain physical and spiritual connections with their ancestors, bridging time and memory,” study author Hirofumi Matsumura with Sapporo Medical University in Japan said in an email.
Dating methods used on the mummies could have been more robust and it’s not yet clear that mummies were consistently smoke-dried across all these locations in southeastern Asia, said human evolution expert Rita Peyroteo Stjerna with Uppsala University in Sweden, who was not involved with the research.
The findings offer “an important contribution to the study of prehistoric funerary practices,” she said in an email.
Mummies are far from a thing of the past. Even today, Indigenous communities in Australia and Papua New Guinea smoke-dry and mummify their dead, scientists said.
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The AP is solely responsible for all content.

