Science (general)
Please review each article prior to use: grade-level applicability and curricular alignment might not be obvious from the headline alone.
What happens when your immune system hijacks your brain
7 minute read Preview Monday, Nov. 24, 2025Author goes far and wide on quest to document all plants native to Manitoba
7 minute read Preview Saturday, Nov. 15, 2025Rare red auroras dazzle as part of Manitoba light show
3 minute read Preview Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025Greenwashing rules to be scaled back, but scope of change remains unclear
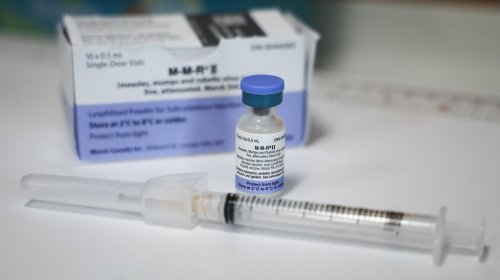
5 minute read Preview Wednesday, Nov. 12, 2025How Canada can regain its measles elimination status
6 minute read Preview Wednesday, Nov. 12, 2025City tries to get the most bang for its (sewage) buck
4 minute read Preview Friday, Nov. 7, 2025Three scientists at US universities win Nobel Prize in physics for advancing quantum technology
6 minute read Preview Wednesday, Oct. 15, 2025Big Tobacco and Big Oil are eerily similar. One knowingly produces a product that slowly but surely kills its consumers. The other knowingly produces a product that surely but not slowly kills the planet.
Only moratorium can save moose population: MWF
4 minute read Preview Wednesday, Sep. 24, 2025Another subdivision, another city problem
5 minute read Preview Tuesday, Sep. 23, 2025Wildfires like this aren’t normal. Stop trying to normalize them.
“Bring a pair of pants and a sweater to Clear Lake — it’s unseasonably cool because of the wildfires.” That was just one of those meteorological idiosyncrasies, attempting to reach back deep into long-forgotten geography lessons, that may seem obvious to those on the Prairies. But for the outsider, a visitor from Toronto, and indeed a relative newcomer to Canada, it was certainly a shock, and a stark reminder that I would be flying into a province still under a state of emergency, which had until recently been decimated by wildfires. It was also an introduction into what may be considered ‘normal’.
Visiting Manitoba this August was extraordinary — the people most certainly lived up to the “friendly” billing that adorns the licence plates, and the scenery of Riding Mountain National Park was worth the trip alone. However, there were a number of topics of conversation that made me question what I had come to know as accepted wisdom.
Talk about fishing restrictions, Indigenous rights, oil and gas permeated discussions, with healthy, good spirited debates. But for me, the most vexing issue was wildfires. More specifically, the extent of their aftermath, effects, and associated restrictions, have become normalized.
On World Rhino Day, South Africa marks progress but still loses a rhino daily to poachers
5 minute read Preview Wednesday, Oct. 15, 2025Ralliers decry Kinew’s pro-pipeline policy
4 minute read Preview Saturday, Sep. 20, 2025Will electric tractors gain traction? At a pilot event for farmers, researchers see possibilities
7 minute read Preview Friday, Oct. 10, 2025After summer evacuation, northern students ready to hit the books
4 minute read Preview Friday, Sep. 19, 2025Province creates hunting buffer zone on Bloodvein First Nation
3 minute read Preview Monday, Sep. 15, 2025Province accuses mining company of negligence in Lynn Lake wildfire
3 minute read Preview Monday, Sep. 15, 2025Very hungry caterpillars very good for biodiversity
5 minute read Preview Saturday, Sep. 13, 2025Nation building needs research — not just infrastructure
5 minute read Saturday, Sep. 13, 2025Living through the second Trump administration as a Canadian has been likened, by one commentator, to a teenager being kicked out of the house. We must grow up fast and deal with the fact that we can now only rely on ourselves. So, the federal government is moving fast on files related to security, sovereignty and connectivity. The Liberals passed Bill C-5 to expedite projects that will help Canadians live on our own. Wonderful.
But.
In our rush forward, we cannot overlook the power of nation-building research, which must go hand-in-glove with these infrastructure projects. Research and infrastructure are not competing priorities: they are essential partners in nation-building.
Bill C-5, the Building Canada Act, grants the federal government sweeping powers to quickly build large projects that help goods move faster and more easily. This act intends to strengthen our security, autonomy, resilience and advance the interests of Indigenous Peoples. But there can be no nation-building without nation-building research.
Residents pour cold water on proposed development in St. Vital
5 minute read Preview Friday, Sep. 12, 2025For elders with dementia, youth with anxiety, or evacuees coping with displacement, smoke is not just a public health irritant. It’s an accelerant for mental health issues.
You can’t put an N95 on your brain. You can’t tell your nervous system to calm down when the air outside looks like dusk at noon.
For older adults, people with asthma, families on fixed incomes, or those living in crowded apartments or trailers, wildfire season in Manitoba is more than just a nuisance. It’s a trigger. Of breathlessness. Of panic. Of helplessness.
And every year, the advice is the same: